Statistical modeling and analysis for state estimation in electrical power distribution grids
B01 addresses statistical challenges caused by the integration of renewable energies and the dismantling of conventional power plants with simultaneous electrification of heating and transport sectors. It develops methods for data acquisition and monitoring to design smart distribution grids. In the long run, new experimental designs for nonlinear state space models and new monitoring procedures will be developed for the optimal resilient and robust operation of electrical power distribution grids.
Project Leaders
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller
Department of Statistics -Chair of Statistics with Applications in Engineering Sciences
TU Dortmund University
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christian Rehtanz
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology - Institute of Energy Systems, Energy Efficiency and Energy Economics
TU Dortmund University
Summary
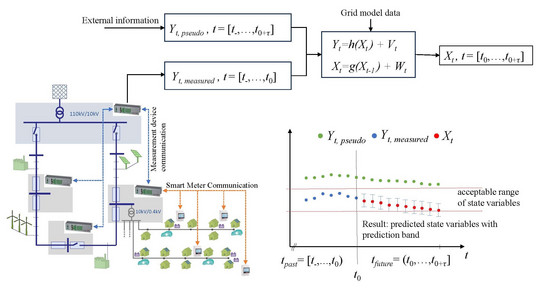
Integrating renewable energy conversion systems and dismantling conventional power plants, while simultaneously electrifying the heating and transport sectors, creates new challenges in the planning and operation of electrical power distribution grids. A key functionality for efficient grid operation and usage is the estimation and prediction of the operational states in terms of voltages and power flows.
Classical state estimation techniques currently in use estimate the state variables at a single point in time. This is achieved by utilizing a sufficiently large number of measurements of spatially distributed sensors, which are time-synchronized within certain limits, and assuming a steady-state behavior of the measured values in a specific time interval of several seconds. However, in distribution grids, the number of spatially distributed sensors is significantly lower in comparison to transmission grids, where state estimation are ubiquitous in use. The measurements on distribution level have typically a lower temporal resolution and the steady-state assumption significantly reduces accuracy due to the high volatility of loads and feed-ins. Additionally, due to the limited number of measurements at sensors, less accurate pseudo-measurement values must be incorporated to achieve observability. Such pseudo-measurements are values derived from secondary data replacing a missing measurement. They are for instance obtained from weather reports to get the electrical input of wind power plants or photovoltaic systems, which might not be measured directly.
The first objective of this project is to design new methods which incorporate the temporal evolution of measured values and the formation of pseudo-measured values, as well as the spatial distribution of measurements, including correlations, into the estimation process. We will achieve this goal by determining important input variables, employing realistic model assumptions, and developing appropriate filtering methods. Specifically, we will relax the common normality assumption, which is unrealistic for electrical power distribution grids. This will lead us to new statistical approaches for the nonlinear state space models typically used in distribution grids, enabling robust estimation under highly volatile conditions.
Furthermore, on the distribution grid level, we need to ensure that voltage or power flows are kept within defined values with a specific confidence level for specific future time intervals. Therefore, our second goal is to determine the prediction intervals (confidence intervals) for the predicted (estimated) future values over a short time interval (e.g., 15 minutes) and to develop online change-point methods for detecting critical situations where the voltage or power flow will exceed critical values in the upcoming time interval. Expanding this time interval from short-term to daily operation is the long-term goal of the project.
To guarantee the required accuracy and probability, an optimal mix of sensors and different types of pseudo-measurements needs to be determined, and we will identify the minimum number of sensor measurements and their placement in medium and low-voltage networks. Additionally, we will determine optimal estimation intervals for the required accuracy. In a further step, the topology of the underlying grid model will be validated. Changes in the grid topology lead to modeling errors, which provide significant practical problems in today's analysis of distribution grids. To address these issues, we will develop new online change-point methods for detecting changes in the network topology that were not communicated to the network operator in a timely manner.
Dohme, H., Malchercyzk, D., Leckey, K., Müller, C. H. (2024). K-depth tests for testing simultaneously independence and other model assumptions in time series. Communications in Statistics - Simulation and Computation, 1–19. DOI: 10.1080/03610918.2024.2413905.



